限流
1、固定窗口
首先维护一个计数器,将单位时间段当做一个窗口,计数器记录这个窗口接收请求的次数。
当次数少于限流阀值,就允许访问,并且计数器+1
当次数大于限流阀值,就拒绝访问。
当前的时间窗口过去之后,计数器清零。
假设单位时间是1秒,限流阀值为3。在单位时间1秒内,每来一个请求,计数器就加1,如果计数器累加的次数超过限流阀值3,后续的请求全部拒绝。等到1s结束后,计数器清0,重新开始计数。
优点:
1、实现简单,代码好实现,单机可用Atomic 等原子类、分布式集群可以用Redis
缺点:
1、限流机制不够平滑,如每秒允许请求100个请求,在第一毫秒内就请求了100个请求,此后都开始限流,导致剩余窗口内的所有请求都会被拒绝
2、在最后1个毫秒内请求了100个请求,下一个毫秒开始新的时间窗口,计数清0,此时又涌入了100个请求,虽说固定时间窗口内没有超过阈值,但是全局看来,这两个毫秒内就涌入了200个请求
实现:
````
@Bean(name = "apiLimitRedisScript")
public DefaultRedisScript<Long> apiLimitRedisScript() {
DefaultRedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptText(apiLimitScriptStr());
redisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
return redisScript;
}
private static String apiLimitScriptStr() {
return "local key = KEYS[1]\n" +
"local a1 = ARGV[1]\n" +
"local a2 = ARGV[2]\n" +
"local count = tonumber(a1)\n" +
"local time = tonumber(a2)\n" +
"\n" +
"if key == nil or count == nil or time == nil then\n" +
" error(\"param is null\")\n" +
"end\n" +
"\n" +
"local current = redis.call('get', key);\n" +
"if current and current ~= nil and tonumber(current) > count then\n" +
" return tonumber(current)\n" +
"end\n" +
"current = redis.call('incr', key);\n" +
"if tonumber(current) == 1 then \n" +
" redis.call('EXPIRE',key,time)\n" +
"end\n" +
"return tonumber(current)";
}
/**
* 固定窗口
* @param point
* @param apiLimit
*/
private void doLimit(JoinPoint point, ApiLimit apiLimit){
log.info("ApiLimitAspect:限流开始:{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(apiLimit));
int time = apiLimit.time();
int num = apiLimit.num();
if(time <= 0 || num <= 0){
throw new BusinessException("访问过于频繁,请稍候再试");
}
//限流类型
ApiLimitType apiLimitType = apiLimit.apiLimitType();
String limitKey = null;
if(ApiLimitType.KEY.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, apiLimit.keyPre());
}else if(ApiLimitType.URL.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
HttpServletRequest request = getRequest();
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, request.getRequestURI());
}else if(ApiLimitType.IP.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
HttpServletRequest request = getRequest();
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, request.getRequestURI()) + ":" + IpUtils.getIpAddr(request);
}else if(ApiLimitType.USERID.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
HttpServletRequest request = getRequest();
TmpUser user = ApiLimitUtils.getUser();
if(null == user || null == user.getId()){
throw new BusinessException(MsgUtils.getMessage(ErrorCodes.SYS_USER_USERINFO_EMPTY));
}
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, request.getRequestURI()) + ":" + user.getId();
}else if(ApiLimitType.APPID.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
HttpServletRequest request = getRequest();
String appId = request.getHeader("appId");
if(StrUtil.isBlank(appId)){
throw new BusinessException("appId 不能为空");
}
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, request.getRequestURI()) + ":" + appId;
}
log.info("ApiLimitAspect:limitKey:{}", limitKey);
Long maxNumber = stringRedisTemplate.execute(apiLimitRedisScript, ListUtil.toList(limitKey), String.valueOf(num),String.valueOf(time));
log.info("ApiLimitAspect:maxNumber:{}:maxNumber:{}",limitKey,maxNumber);
if (null != maxNumber && maxNumber > num) {
log.info("ApiLimitAspect:limitKey:{}:limitResult:访问过于频繁,请稍候再试",limitKey);
throw new BusinessException("访问过于频繁,请稍候再试");
}
}
````
2、滑动窗口
在固定时间窗口的基础上进行优化,对大的时间窗口进行划分,每个小窗口对应大窗口中的不同时间点,每个窗口独立计数。随时间的变化,小窗口随之平移,并且重置/舍弃过期的小窗口,每个小窗口的计数器相加,不超过大窗口的限流limit,即限流阈值之内。
优点:
1、避免了固定窗口算法可能出现的窗口切换时的流量峰值,使得流量控制更为平滑
缺点:
1、对时间区间精度要求越高,算法所需的空间容量越大,需要更多的计算和存储资源
2、还是存在限流不够平滑的问题。例如:限流是每秒100个,在第一毫秒发送了100个请求,达到限流,剩余窗口时间的请求都将会被拒绝
`````
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @author YY-帆S
* @Date 2024/3/26 15:04
*/
public class SlidingWindowRateLimiter {
private int windowSize; //时间窗口大小, Unit: s
private int slotNum; //用于统计的子窗口数量,默认为10
private int slotTime; //子窗口的时间长度, Unit: ms
private int limit; //限流阈值
/**
* 存放子窗口统计结果的数组
* note: counters[0]记为数组左边, counters[size-1]记为数组右边
*/
private AtomicInteger[] counters;
private long lastTime;
//初始化
public SlidingWindowRateLimiter(int windowSize, int limit, int slotNum) {
this.windowSize = windowSize;
this.limit = limit;
this.slotNum = slotNum;
// 计算子窗口的时间长度: 时间窗口 / 子窗口数量
this.slotTime = windowSize * 1000 / slotNum;
this.lastTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.counters = new AtomicInteger[slotNum];
resetCounters();
}
public SlidingWindowRateLimiter(int windowSize, int limit) {
this(windowSize, limit, 10);
}
private void resetCounters() {
for (int i = 0; i < counters.length; i++) {
counters[i] = new AtomicInteger(0); // 每个数组元素都是一个新的AtomicInteger实例
}
}
/**
* 限流请求
* @return
*/
public synchronized boolean tryAcquire() {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 计算滑动数, 子窗口统计时所对应的时间范围为左闭右开区间, 即[a,b)
int slideNum = (int) Math.floor((currentTime - lastTime) / slotTime);
// 滑动窗口
slideWindow(slideNum);
// 统计滑动后的数组之和
int sum = Arrays.stream(counters).mapToInt(AtomicInteger::get).sum();
// 以达到当前时间窗口的请求阈值, 故被限流直接返回false
if (sum >= limit) {
return false;
} else { // 未达到限流, 故返回true
counters[slotNum - 1].incrementAndGet();
return true;
}
}
/**
* 将数组元素全部向左移动num个位置
*
* @param num
*/
private void slideWindow(int num) {
if (num == 0) {
return;
}
// 数组中所有元素都会被移出, 故直接全部清零
if (num >= slotNum) {
resetCounters();
} else {
// 对于a[0]~a[num-1]而言, 向左移动num个位置后, 则直接被移出了
// 故从a[num]开始移动即可
for (int index = num; index < slotNum; index++) {
// 计算a[index]元素向左移动num个位置后的新位置索引
int newIndex = index - num;
counters[newIndex] = counters[index];
counters[index].getAndSet(0);
}
}
// 更新时间
lastTime = lastTime + num * slotTime;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//例子:5s内只能有50个请求
SlidingWindowRateLimiter rateLimiter = new SlidingWindowRateLimiter(5, 50);
int allNum = 3; // 请求总数
int passNum = 0; // 通过数
int blockNum = 0; // 被限流数
//模拟连续请求
for (int i = 0; i < allNum; i++) {
if (rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
passNum++;
} else {
blockNum++;
}
}
System.out.println("请求总数: " + allNum + ", 通过数: " + passNum + ", 被限流数: " + blockNum);
// 延时以准备下一次测试
Thread.sleep(5000);
allNum = 100;
passNum = 0;
blockNum = 0;
//模拟连续请求
for (int i = 0; i < allNum; i++) {
if (rateLimiter.tryAcquire()) {
passNum++;
} else {
blockNum++;
}
}
System.out.println("请求总数: " + allNum + ", 通过数: " + passNum + ", 被限流数: " + blockNum);
}
}
`````
3、漏桶算法
该算法使用“桶”来比喻,不断有水(请求)进入桶内并以固定速率进行处理,模拟桶中的“泄漏”,当加水速度>漏水速度时,直到某一个时刻,存储桶己满,新的请求将被丢弃,直到有可用空间。
优点:
1、平滑流量输出:漏桶算法可以有效地平滑网络上的突发流量,为网络提供一个稳定的流量输出。通过将流量注入到漏桶中,并根据桶的漏水速率来控制流量的输出,可以确保流量的平稳性。
2、 防止流量冲击:由于漏桶具有缓存功能,当流量突发超过设定阈值时,超出的部分可以被暂存在桶中/直接丢弃,从而避免了流量冲击对系统造成的压力。
缺点:
1、灵活性相对较差:漏桶算法的速率是恒定的,不能根据实际需要动态调整。这可能导致在某些情况下,系统无法充分利用网络资源,造成一定的资源浪费。
2、无法应对突发流量:由于漏桶的出口速度是固定的,在面对突发流量时,即使是在流量较小的情况下,仍然是以固定速率处理,也无法以更快的速度处理请求
````
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* @author YY-帆S
* @Date 2024/3/26 22:46
*/
@Slf4j
public class LeakyBucketRateLimiter {
private AtomicInteger bucketLevel; // 当前桶中的请求数量
private int capacity; // 桶的容量
private long leakRate; // 漏水速率,单位:请求/秒
private long lastLeakTime; // 上一次漏水的时间戳
public LeakyBucketRateLimiter(int capacity, long leakRate) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.leakRate = leakRate;
this.bucketLevel = new AtomicInteger(0);
this.lastLeakTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public synchronized boolean tryAcquire() {
// 获取当前时间
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//流出时间
long elapsedTime = currentTime - lastLeakTime;
//计算流出的水量 = (当前时间 - 上次时间) * 出水速率
long leaked = (long) (elapsedTime * (leakRate / 1000.0));
//只有有流出水才更新时间戳,不然会漏不出水
if (leaked > 0) {
//计算桶内水量 = 桶内当前水量 - 流出的水量
int newLevel = Math.max(0, bucketLevel.get() - (int) leaked);
bucketLevel.set(newLevel);
//更新上次漏水时间戳
lastLeakTime = currentTime;
}
// 尝试将请求加入桶中
if (bucketLevel.get() < capacity) {
bucketLevel.incrementAndGet();
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
LeakyBucketRateLimiter limiter = new LeakyBucketRateLimiter(1, 1); // 容量为1,漏水速率为1请求/秒
// 模拟发送请求
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
if (limiter.tryAcquire()) {
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 获得了许可,执行操作。");
} else {
log.info(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 请求被拒绝。");
}
}).start();
//模拟执行时间
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
}
````
4、令牌桶
与漏桶算法相反,系统以固定的速率往桶里放入令牌,称为令牌桶,如果有请求需要这个令牌,这可以从桶里拿一个,拿到了令牌即允许放行,直到令牌被拿完即令牌不足,则请求需等待或被丢弃。
令牌的数量与时间和发放速率强相关,随着时间流逝,系统会不断往桶里放入更多的令牌,如果放令牌的速度比拿令牌的速度快,则令牌桶最终会被放满
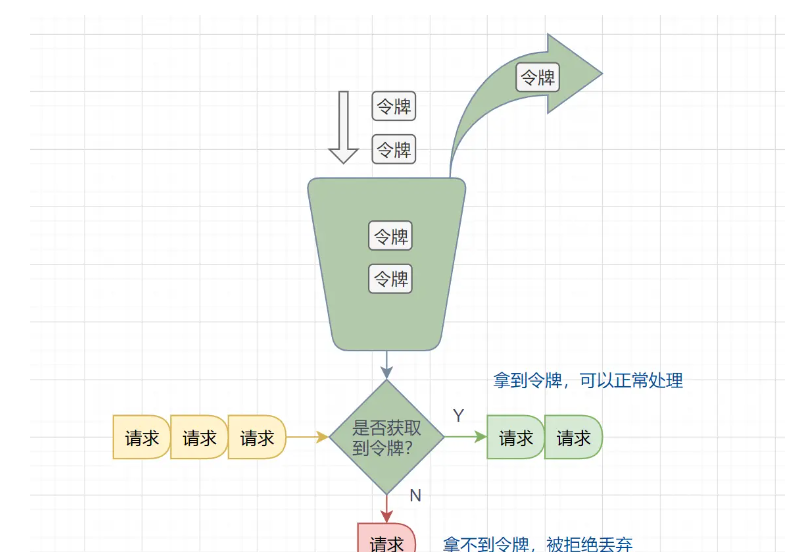
优点:
1、应对突发流量:令牌桶算法允许流量突发,当桶满时,系统能以最大的速度处理请求
2、灵活性:算法允许根据实际需求调整令牌生成速率和令牌桶大小等参数
3、限制平均速度:长期运行的服务,数据处理速度最终会动态平衡,限制在预定义的平均速率,即生成令牌的速率
缺点:
1、导致过载的可能性:要控制令牌的产生速度,如果令牌产生的速度过快,可能会导致大量的突发流量,这可能会使网络或服务过载。
2、内存资源限制:令牌桶需要一定的存储空间来保存令牌,可能会导致内存资源的浪费。且对于特别频繁的请求,令牌桶算法可能会占用较多的计算资源,增加系统负担。
3、实现稍复杂:相比于计数器等其他限流算法,令牌桶算法的实现稍微复杂一些
````
@Bean(name = "tokenBucketLimitScript")
public DefaultRedisScript<Long> tokenBucketLimitScript() {
return new DefaultRedisScript<>(TOKEN_BUCKET_LIMIT_SCRIPT,Long.class);
}
private static final String TOKEN_BUCKET_LIMIT_SCRIPT = "local tokens_key = KEYS[1]\n" +
"local timestamp_key = KEYS[2]\n" +
"local rate = tonumber(ARGV[1])\n" +
"local capacity = tonumber(ARGV[2])\n" +
"local now = tonumber(ARGV[3])\n" +
"local requested = tonumber(ARGV[4])\n" +
"local fill_time = capacity/rate\n" +
"local ttl = math.floor(fill_time*2)\n" +
"local last_tokens = tonumber(redis.call('get', tokens_key))\n" +
"if last_tokens == nil then\n" +
" last_tokens = capacity\n" +
"end\n" +
"local last_refreshed = tonumber(redis.call('get', timestamp_key))\n" +
"if last_refreshed == nil then\n" +
" last_refreshed = 0\n" +
"end\n" +
"local diff_time = math.max(0, now-last_refreshed)\n" +
"local filled_tokens = math.min(capacity, last_tokens+(diff_time*rate))\n" +
"local allowed = filled_tokens >= requested\n" +
"local new_tokens = filled_tokens\n" +
"local allowed_num = 0\n" +
"if allowed then\n" +
" new_tokens = filled_tokens - requested\n" +
" allowed_num = 1\n" +
"end\n" +
"if ttl > 0 then\n" +
" redis.call('setex', tokens_key, ttl, new_tokens)\n" +
" redis.call('setex', timestamp_key, ttl, now)\n" +
"end\n" +
"return allowed_num\n";
/**
* 令牌桶限流
* @param stringRedisTemplate redis
* @param key 自定义key
* @param rate 每秒填充速率
* @param capacity 令牌桶最大容量
* @param tokens 每次访问消耗几个令牌
* @return true 允许访问 false 不允许访问
*/
public boolean tokenBucketLimitAllowed(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate,RedisScript<Long> redisScript, String key, int rate, int capacity, int tokens){
Object result = stringRedisTemplate.execute(redisScript,
getTokenBucketLimitKey(key),rate, capacity,
Instant.now().getEpochSecond(), tokens);
System.out.println("result:"+result);
return SUCCESS_FLAG.equals(result);
}
private List<String> getTokenBucketLimitKey(String key){
String prefix = "api_aop_lm_tb:"+key;
String tokenKey = prefix + ":tokens";
String timestampKey = prefix + ":timestamp";
return Arrays.asList(tokenKey, timestampKey);
}
private static final Long SUCCESS_FLAG = 1L;
/**
* 令牌桶
* @param point
* @param apiLimit
*/
private void doLimitTokenBucket(JoinPoint point, ApiLimit apiLimit){
log.info("ApiLimitAspect:限流开始:{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(apiLimit));
int time = apiLimit.time();
int num = apiLimit.num();
if(time <= 0 || num <= 0){
throw new BusinessException("访问过于频繁,请稍候再试");
}
//限流类型
ApiLimitType apiLimitType = apiLimit.apiLimitType();
String limitKey = null;
if(ApiLimitType.KEY.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, apiLimit.keyPre());
}else if(ApiLimitType.URL.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
HttpServletRequest request = getRequest();
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, request.getRequestURI());
}else if(ApiLimitType.IP.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
HttpServletRequest request = getRequest();
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, request.getRequestURI()) + ":" + IpUtils.getIpAddr(request);
}else if(ApiLimitType.USERID.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
HttpServletRequest request = getRequest();
TmpUser user = ApiLimitUtils.getUser();
if(null == user || null == user.getId()){
throw new BusinessException(MsgUtils.getMessage(ErrorCodes.SYS_USER_USERINFO_EMPTY));
}
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, request.getRequestURI()) + ":" + user.getId();
}else if(ApiLimitType.APPID.getType().equals(apiLimitType.getType())){
HttpServletRequest request = getRequest();
String appId = request.getHeader("appId");
if(StrUtil.isBlank(appId)){
throw new BusinessException("appId 不能为空");
}
limitKey = String.format(CacheConstants.API_LIMIT_PRE_KEY, request.getRequestURI()) + ":" + appId;
}
log.info("ApiLimitAspect:limitKey:{}", limitKey);
boolean b = ApiLimitUtils.tokenBucketLimitAllowed(stringRedisTemplate,tokenBucketLimitScript, limitKey, time, num, 1);
if(!b){
log.info("ApiLimitAspect:limitKey:{}:limitResult:访问过于频繁,请稍候再试",limitKey);
throw new BusinessException("访问过于频繁,请稍候再试");
}
}
令牌桶V2
增加:周期时间内最大访问量 做全局限制
````
/**
* 判断是否允许访问
*@param id 这次获取令牌桶的id
*@param rate 每秒填充速率
*@param capacity 令牌桶最大容量
*@param tokens 每次访问消耗几个令牌
*@param maxCount 周期时间内最大访问量
*@return true 允许访问 false 不允许访问
*/
public boolean isAllowed(String id,int rate,int capacity,int tokens,int maxCount){
RedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>(SCRIPT,Long.class);
Object result = redisTemplate.execute(redisScript,
getKey(id),rate, capacity,
Instant.now().getEpochSecond(), tokens,maxCount);
return SUCCESS_FLAG.equals(result);
}
private List<String> getKey(String id){
String prefix = "limiter:"+id;
String tokenKey = prefix + ":tokens";
String timestampKey = prefix + ":timestamp";
String countKey = prefix + ":count";
return Arrays.asList(tokenKey, timestampKey,countKey);
}
private static final String SCRIPT = "local tokens_key = KEYS[1]\n" +
"local timestamp_key = KEYS[2]\n" +
"local count_key = KEYS[3]\n" +
"local rate = tonumber(ARGV[1])\n" +
"local capacity = tonumber(ARGV[2])\n" +
"local now = tonumber(ARGV[3])\n" +
"local requested = tonumber(ARGV[4])\n" +
"local min_max = tonumber(ARGV[5])\n" +
"local fill_time = capacity/rate\n" +
"local ttl = math.floor(fill_time*2)\n" +
"local has_count = tonumber(redis.call('get', count_key))\n" +
"if has_count == nil then\n" +
" has_count = 0\n" +
"end\n" +
"if has_count >= min_max then\n" +
"return 0\n" +
"end\n" +
"local last_tokens = tonumber(redis.call('get', tokens_key))\n" +
"if last_tokens == nil then\n" +
" last_tokens = capacity\n" +
"end\n" +
"local last_refreshed = tonumber(redis.call('get', timestamp_key))\n" +
"if last_refreshed == nil then\n" +
" last_refreshed = 0\n" +
"end\n" +
"local diff_time = math.max(0, now-last_refreshed)\n" +
"local filled_tokens = math.min(capacity, last_tokens+(diff_time*rate))\n" +
"local allowed = filled_tokens >= requested\n" +
"local new_tokens = filled_tokens\n" +
"local allowed_num = 0\n" +
"if allowed then\n" +
" new_tokens = filled_tokens - requested\n" +
" allowed_num = 1\n" +
"end\n" +
"if ttl > 0 then\n" +
" redis.call('setex', tokens_key, ttl, new_tokens)\n" +
" redis.call('setex', timestamp_key, ttl, now)\n" +
"end\n" +
"local count_ttl = tonumber(redis.call('ttl',count_key))\n" +
"if count_ttl < 0 then\n" +
" count_ttl = fill_time\n" +
"end\n" +
"redis.call('setex', count_key,count_ttl , has_count+1)\n" +
"return allowed_num\n";
}
````

